It didn’t start with a loss.
It started with confidence.
A message popped up on my phone late one evening:
“Bhai, yeh stock pakka chalega. Sab bol rahe hain.”
The next morning, the market opened strong. Green numbers everywhere. Screens glowing with promise. For a moment, it felt like the market was finally listening. No charts. No calculations. Just belief.
A few days later, the same screen looked different. Red replaced green. Notifications turned silent. The confidence that felt so natural earlier now felt heavy. Decisions were no longer about opportunity—they were about hope. “Thoda aur ruk jaata hoon… shayad wapas aa jaaye.”
That moment—when hope replaces logic—is where many trading journeys quietly go wrong.
Many people enter the stock market hoping to make quick profits. They invest based on tips from friends, social media posts, or what is currently trending. When the market moves against them, confusion, anxiety, and disappointment often follow. Over time, trading starts to feel more like chance than a process based on knowledge and planning.
A few months ago, I spoke with a colleague named Rakesh who had recently started trading on his own. In one volatile week, he lost close to ₹35,000 after buying stocks purely on online recommendations—without checking charts, fundamentals, or setting stop losses. When prices fell, he held on, hoping they would recover, only to exit later at a bigger loss. What stood out was not the loss itself, but the fact that he never had a clear reason for entering or exiting the trades.
The real issue isn’t the market.
It’s the absence of a plan.
Without a clear strategy, trading decisions are driven by fear during market declines and excitement during market rallies. This emotional cycle makes results unpredictable and stressful.
This is where a trading strategy becomes essential. A strategy defines why you enter a trade, when you exit, and how much you are willing to risk. Professional traders don’t rely on luck or tips—they rely on systems that protect them from their own emotions.
In this blog, you’ll learn how trading strategies work, explore different trading styles, and understand how to choose one that aligns with your experience, mindset, and approach to the market.
2. What Is a Trading Strategy?
A clear plan that directs when and how to trade the markets is called a trading strategy. It has nothing to do with making quick money or forecasting pricing. Rather, it provides you with a reliable way to make rational and composed conclusions.
Being disciplined, limiting your losses, and allowing those tiny wins to accumulate over time are the key components of good trading, not winning every deal. This discipline is introduced by a sound strategy, which specifies exactly what to trade, when to enter, how much money to risk, and when not to trade at all.
Trading is emotional without one. Fear, greed, news, and abrupt price changes all cause people to react. With a strategy, every trade has a purpose, and every result, be it profit or loss, is part of a bigger, well-thought-out plan.

Core Elements of a Successful Trading Strategy
Risk Management
The foundation of profitable trading is managing risk. A trader must determine how much they are willing to lose overall and on a single trade before considering making money. This entails determining the highest loss they can bear, setting a stop-loss, and selecting the appropriate trade size.
Experienced traders focus first on protecting their money. They understand that staying in the market for the long term is what gives them the chance to grow their profits over time.
Entry and Exit Rules
Exactly when to take a trade is explained by clear entry guidelines. This could be determined by trading volume, price movement, indicators, or a mix of these. Exit criteria that specify when to accept a loss and when to take profits are equally important.
Experienced traders don’t continue to trade because they are hesitant or hopeful. They exit deals according to precise, predetermined guidelines, which helps keep the process disciplined and consistent by removing emotion from decision-making.
Time Horizons
Every trading technique has a time limit. While some traders hold trades for days, weeks, or even months, others concentrate on price changes within a single day. The frequency of trades, the amount of risk involved, and the degree of stress a trader feels are all impacted by this time frame.
Successful traders select a time period based on their risk tolerance, daily routine, and personality. They don’t push themselves into a trading style that is hurried, demanding, or challenging to control.
Discipline and Consistency
What distinguishes novice traders from seasoned ones is discipline. If a strategy is not consistently implemented, it will be ineffective. Proficient traders acknowledge that losses are a necessary element of trading and refrain from trading excessively, attempting to quickly recover losses, or altering their strategy following a poor deal.
This discipline is what eventually transforms a sound approach into consistent, long-term outcomes. To put it simply, a trading strategy is your market guide. It provides you with control, structure, and clear direction, all necessary for long-term trading success—but it does not guarantee profits.

3. Key Professional Trading Strategies
Professional traders do not rely on one single “best” strategy. Instead, they choose an approach that fits their personality, available time, and understanding of how markets move. Every strategy has its own strengths and limits, and none of them work without discipline and proper risk control.
A. Position Trading
Position trading is a long-term approach that seeks to identify important market movements over several days, weeks, or even months. Traders hold onto their holdings during normal ups and downs in order to profit from large, sustained market movements.
Position traders often utilize charts with longer time frames, such as daily and weekly charts. Larger factors are also considered, such as long-term price trends, robust or weak industries, and economic cycles. Dealers usually have greater conviction in each trade, despite the fact that fewer are made. Stop losses are placed wider apart to give the trade enough time and space to expand.
Pros and Cons
The main advantage of this method is that fewer trades and less screen time result in fewer emotional reactions. Additionally, trading expenditures are decreased because deals are not made frequently. But this strategy requires persistence and the ability to remain calm in the face of transient price swings. Losses can be unpleasant if risk is not adequately managed.
Ideal Trader Profile
This approach works well for traders who are comfortable holding transactions for extended periods of time, comprehend the larger picture of the market, and are unable to observe the markets every day.
B. Swing Trading
The goal of swing trading is to profit from brief to medium-term price movements, which typically last a few days to a few weeks. Profiting from market fluctuations rather than long-term trends is the aim.
Technical analysis is mostly used by swing traders to identify entry points close to regions of support or resistance and to exit when momentum slows or price targets are reached. This approach frequently incorporates price patterns, momentum indicators, and trend analysis. Instead of being constantly monitored, trades are typically evaluated once a day.
Pros and Cons
A decent balance between trading opportunities and time commitment is provided by swing trading. Compared to position trading, it offers additional trading opportunities without the pressure and pace of day trading. The primary disadvantage is exposure to unforeseen news and overnight risk, which can result in large price movements against a transaction.
Ideal Trader Profile
This technique is appropriate for traders who desire a clear, structured approach without always staring at the computer, seek flexibility, and can review charts once a day.
C. Day Trading
Opening and closing every trade on the same trading day is known as day trading. There are no overnight positions.
Day traders concentrate on price changes during the day and use shorter time frames, including 5- or 15-minute charts. Technical setups, volume, and short-term momentum all influence trades. Decisions must be taken swiftly and confidently, and risk is kept to a minimum.
Pros and Cons
The main benefit is that results appear rapidly and there is no nighttime risk. But day trading necessitates intense concentration, emotional restraint, and rigorous discipline. Additionally, the large volume of trades raises mental strain and trading expenses.
Ideal Trader Profile
This approach works best for traders who can dedicate themselves to entire trading hours, make snap judgements, and maintain discipline under duress.
- Price Action Trading
Price action trading doesn’t rely heavily on indicators; instead, it concentrates solely on price movements. Traders research key price levels, candlestick behaviour, and chart patterns.
Market structure, including higher highs, lower lows, breakouts, and price movements at support and resistance areas, is used to inform decisions. The theory is that complicated indicators are unnecessary because the price already displays all available information.

Pros and Cons
Price action trading doesn’t rely heavily on indicators; instead, it concentrates solely on price movements. Traders research key price levels, candlestick behaviour, and chart patterns.
Market structure, including higher highs, lower lows, breakouts, and price movements at support and resistance areas, is used to inform decisions. The theory is that complicated indicators are unnecessary because the price already displays all available information.
Ideal Trader Profile
Ideal for traders who wish to gain an instinctive sense of market movements, have good chart-reading abilities, and prefer simplicity.
E. Algorithmic & Automated Trading
Algorithmic trading executes deals automatically using pre-established rules and algorithms. Human emotion is eliminated from the execution process by these systems.
How It Works
Trading logic is coded using strategies like mean reversion, arbitrage, and trend-following. After it is put into use, the system automatically searches markets and executes deals. Performance is regularly assessed and improved.
Pros and Cons
Consistency and quickness are the primary advantages, particularly in erratic markets. Emotional mistakes are decreased with automation. On the downside, system development requires technical expertise, ongoing testing, and an understanding of market behaviour to avoid over-optimization.
Ideal Trader Profile
Ideal for traders, professionals, or organizations with data, technology, and systematic research capabilities who have a quantitative mindset.
F. News & Event-Driven Trading
This approach focuses on trading market responses to news, economic data, earnings announcements, and significant international events.
In order to position themselves appropriately, traders assess how markets are likely to react to particular occurrences. Because price changes can be abrupt and brief, timing is crucial. Both post-event reactions and pre-event positioning are employed.
Pros and Cons
Because of the increased volatility, there is a strong chance for quick gains. However, because markets might react in an unpredictable way, the dangers are equally important. Abrupt reversals and slippage are frequent.
Ideal Trader Profile
Ideal for traders who can actively manage risk, assimilate information fast, and maintain composure under extremely volatile circumstances.
4. Other Effective Strategies Professionals Use
Trend Trading
Rather than attempting to forecast reversals, trend trading concentrates on trading in the market’s primary direction. Traders enter trades during pullbacks or continuation setups, searching for higher highs and higher lows in an uptrend or lower highs and lower lows in a downtrend.
Allowing profitable trades to occur is this strategy’s strength. However, staying in a trade amid typical pullbacks without pulling out too soon calls for patience and self-control.
Range Trading
When the market fluctuates between distinct levels of support and resistance, range trading is employed. With the expectation that the price would remain within this range, traders purchase near support and sell near resistance.
Because entrance and exit levels are well-defined, risk is easier to manage. Strict stop losses are crucial since this approach gets dangerous when the price moves outside of the range.
Breakout Strategies
The goal of breakout trading is to identify significant price movements that occur when the market surpasses significant benchmarks, such as consolidation zones, prior highs, or prior lows. Increased market involvement and momentum are necessary for these trades.
False signals frequently occur, particularly when trading volume is low, even if breakouts can result in rapid gains. Strict risk control and meticulous confirmation are therefore required.
Scalping
In the fast-paced intraday trading strategy known as scalping, traders make numerous minor trades throughout the day. Profiting from little price changes rather than major trends is the aim.
Accurate entries, rapid execution, and strict risk control are necessary for this strategy. Scalping is best suited for seasoned intraday traders because of its pace, pressure, and greater trading costs.

Quantitative & Statistical Strategies
Data and statistics, not subjective opinion, are the foundation of quantitative and statistical strategy. Rather than depending on market judgments or intuition, traders make decisions using mathematical models and probability.
Pairs trading and mean reversion are two strategies that capitalize on recurring patterns and relationships. Professional and institutional traders who have access to trustworthy data, robust technology, and appropriate processes to test and improve their strategies typically employ these techniques.
5. How to Choose the Right Strategy
Understanding your time availability is the first step in selecting a trading strategy. While swing trading permits review at the end of the day, day trading demands complete focus during market hours. For traders who prefer a longer-term strategy with less screen time, position trading is more appropriate.
Both your emotional disposition and skill level are crucial. Experience, self-control, and the capacity to make frequent decisions without experiencing emotional reactions are necessary for faster techniques. Slower approaches are frequently better for establishing consistency and give more time for examination.
The efficiency of a strategy is also influenced by market selection. Cryptocurrency markets are extremely volatile and sentiment-driven, stocks react significantly to sector trends and earnings, and FX markets are influenced by macroeconomic data. Futures demand stringent risk management because of leverage.
6. Building Your Own Trading Plan
Your decision-making is given structure by a trading plan. It integrates your selected approach with explicit risk guidelines, including position size, stop-loss thresholds, and the highest allowable loss per trade. This guarantees that all trades are scheduled prior to capital commitment.
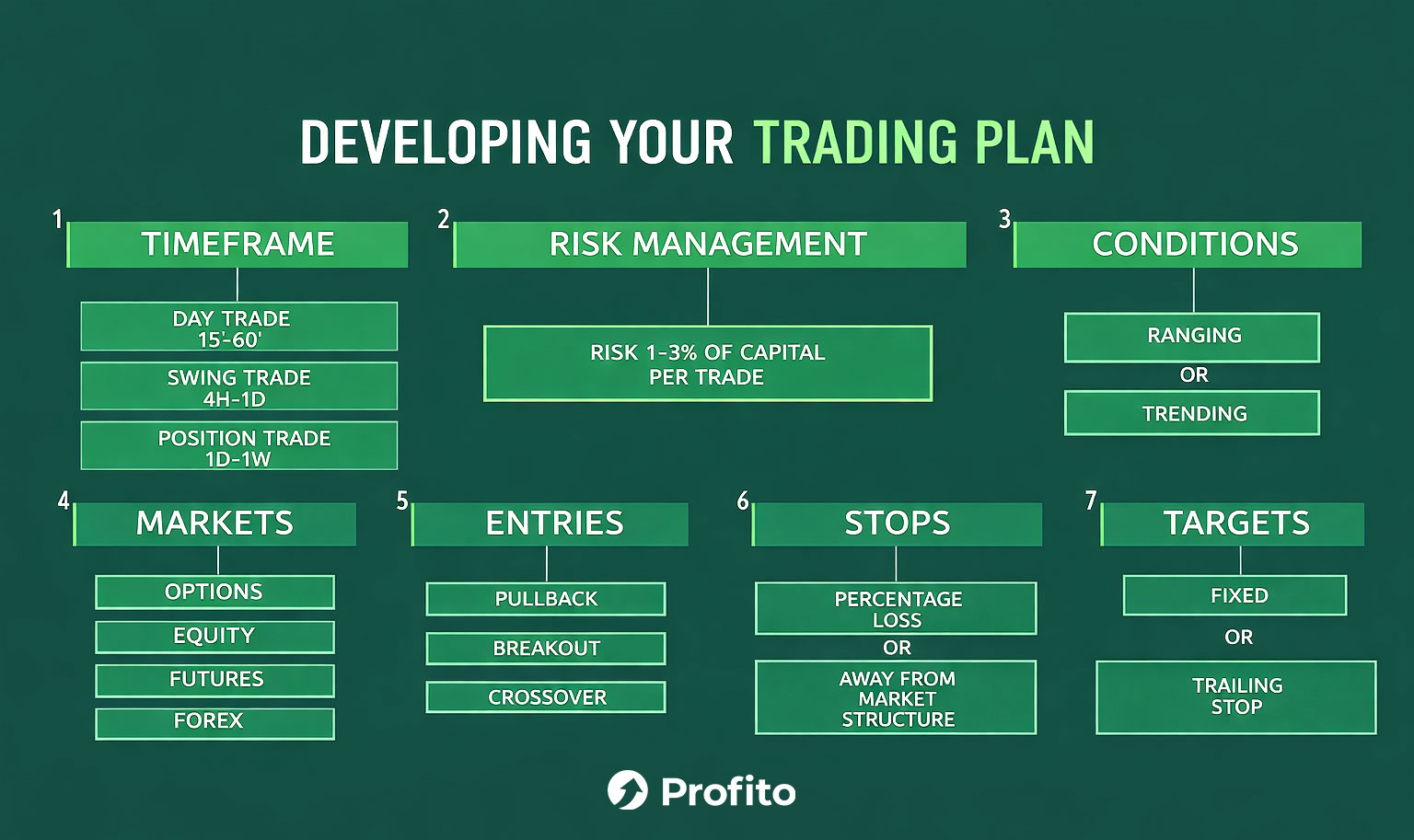
Journaling and backtesting aid in validating your strategy. While a trading record reveals trends in execution, errors, and discipline, a review of historical data demonstrates how a strategy works under various market conditions. This procedure produces quantifiable progress over time.
You can improve your idea without worrying about money if you use a demo account. Before switching to live trading, it helps test timing, execution, and emotional control in actual market situations.
A well-designed trading plan facilitates long-term consistency and transforms concepts into a repeatable practice.
7. Ways for Better Risk Management
Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels
There should be predetermined exit points for every deal. Take-profit goals lock in gains, while stop-loss levels reduce downside risk. Eliminating emotion and preserving consistency can be achieved by defining both before entrance.
Position Sizing Basics
The amount of capital allotted to a single deal is managed by position sizing. Professional traders make sure losses are manageable over time by risking only a tiny portion of their overall money on every position.
Avoiding Over-Leverage
Exposure is increased by leverage, not precision. During typical market volatility, excessive leverage can swiftly erode capital. Trades can go without forced exits when leverage is used conservatively.
Diversifying Trades
Diversification lessens dependence on a particular setup or market. Performance is smoothed, and overall portfolio risk is reduced by distributing transactions among several products or strategies.
Consistency Over Frequency
Better outcomes are not guaranteed by frequent trading. Long-term performance is steadier when high-quality setups are consistently executed with limited risk.
8. Trade Smarter with Expert Financial Guidance
Strategies and setups are only one part of successful trading. True consistency comes from disciplined risk management, precise execution, and informed decision-making built on experience.
At Profito, we support traders and investors with research-driven insights and practical advisory guidance focused on long-term stability rather than short-term speculation. Our approach helps clients gain clarity, manage risk effectively, and trade with confidence instead of emotion.
If you are looking to refine your trading strategy, strengthen risk management, or develop a more structured market approach, expert financial guidance can make a meaningful difference.
Visit profito to explore how Profito can help you trade smarter and invest with greater confidence.
FAQs
- What is a trading strategy, and why is it important?
A trading strategy is a clear plan that defines when to trade, how much to risk, and when to exit. It helps traders make decisions logically instead of emotionally. - Can I trade profitably without a strategy?
Trading without a strategy usually leads to inconsistent results. A strategy provides structure and discipline, which are essential for long-term success. - How do professional traders choose their trading strategy?
Professional traders select strategies based on their personality, time availability, risk tolerance, and understanding of market behavior. - Is there a single best trading strategy that works for everyone?
No. Every strategy has strengths and limitations. What works well for one trader may not suit another. - What is the difference between position trading, swing trading, and day trading?
Position trading focuses on long-term trends, swing trading targets short to medium-term moves, and day trading involves opening and closing trades within the same day. - Which trading style is best for beginners?
Swing trading and position trading are often better for beginners because they allow more time for analysis and involve less emotional pressure. - How important is risk management in trading?
Risk management is critical. Protecting capital allows traders to stay in the market long enough for profits to grow over time. - What is position sizing, and why does it matter?
Position sizing determines how much money is used in each trade. Proper sizing helps limit losses and control overall risk. - What are stop-loss and take-profit levels?
A stop-loss limits losses if the trade goes wrong, while a take-profit locks in gains when the price reaches a target. - What is price action trading?
Price action trading focuses on analyzing price movement, chart patterns, and key levels without relying heavily on indicators. - Are algorithmic and automated trading suitable for individual traders?
They can be, but they require technical knowledge, reliable data, and proper testing. They are more commonly used by experienced and institutional traders. - What risks are involved in day trading?
Day trading involves high mental pressure, fast decision-making, frequent trades, and higher transaction costs. - How do traders handle emotional stress in trading?
By following a clear strategy, managing risk properly, and maintaining discipline regardless of short-term outcomes. - Is backtesting really necessary before live trading?
Yes. Backtesting helps understand how a strategy performs in different market conditions before risking real money. - How long does it take to become a consistently profitable trader?
There is no fixed timeline. Consistency comes from experience, discipline, proper risk management, and continuous learning.







